Automated Deployment to OpenShift Using Jenkins and Webhook
Aug 12, 2018 · 4 Min Read · 2 Likes · 5 Comments
The last post was about defining the pipelines. Now it is time to execute them. Also, at the end, we are going to show how to integrate webhook in your repository, so that for a specific event(like Push, Pull request merge etc) it will trigger the pipelines to automatically deploy the latest code to servers.
Creating python jenkins slave
Most important step before we start using pipeline is to create a Jenkins Slave. For our python execution, we need a python slave to execute step 1-4 described in previous post. There is two ways to do that:
- Way One:
- Go to Manage Jenkins(URL: Jenkins_Url/manage)
- Click on Configure System

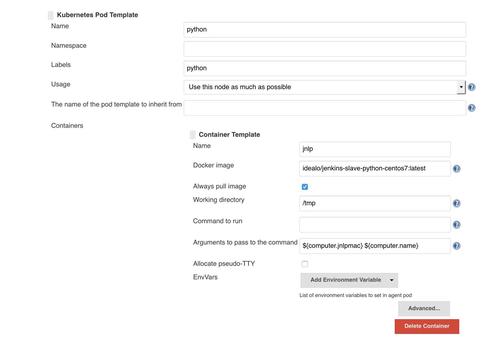
- Then go to bottom of settings, under Kubernetes Pod Template. Then click on Add Pod Template.

- Now add configuration given as the following image:If the image is not clear enough then please use the following dictionary:

{ Name: python Labels: python // click on add container Container Template: { Name: jnlp Docker Image: idealo/jenkins-slave-python-centos7:latest Always pull image: True Working directory: /tmp Arguments to pass to the command: ${computer.jnlpmac}${computer.name} } }- Let us save this configuration by clicking on Save button.
- Way Two: Use this command from idealo’s repository:
oc create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/idealo/jenkins-ci/master/config-map.yamlOr just follow their instructions.
By the way, there are other jenkins python slaves available in github or other opensource repository. Feel free to use any of your choice. I am using this repository, for this demo purpose.
Create build config
We need to import our pipeline to openshift. For that we need to create a Build Config for that. Let’s do that:
apiVersion: v1
kind: BuildConfig
metadata:
labels:
app: python-nginx-pipeline
name: python-nginx-pipeline
spec:
source:
git:
ref: master
uri: <your git repository link>
strategy:
jenkinsPipelineStrategy:
jenkinsfilePath: path/to/Jenkinsfile
type: JenkinsPipeline
triggers:
- github:
secret: secret
type: GitHub
- generic:
secret: secret
type: Generic
- bitbucket:
secret: secret
type: Bitbucket
We can save this as jenkins-pipeline.yaml. You can import this using:
oc project cicd
oc create -f jenkins-pipeline.yaml
Now, if you go to web interface of OpenShift and access in url path OPENSHIFT_URL > console > CI/CD project > browse > pipelines, you should see a new pipeline has been created. You can import the build config directly in openshift web interface as well.
Running pipeline
You can run the pipeline using the Start Pipeline on top right corner of pipeline page. Or you can do that using command line:
oc start-build python-nginx-pipeline
Outcome
Here comes the sweet results of your hard work. You should see the pipeline executions like this:
Before STAGE deployment prompt
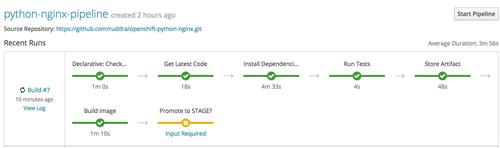
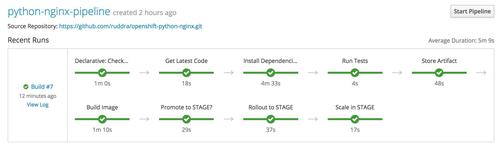
Full pipeline execution
Blue Ocean pipeline
If you go to Blue Ocean(comes build-in) of Jenkins, then go to your latest build, you should see a beautiful pipeline looks like this:
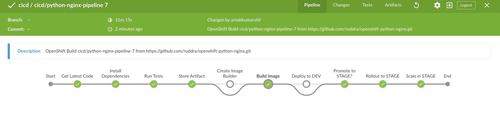
Also if you click on tests, then you should see the recorded result of tests:
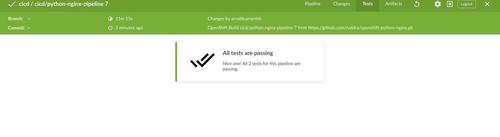
In Artifacts section, you will see pipeline logs and the artifact file which you have stored in Step 4 of previous post:
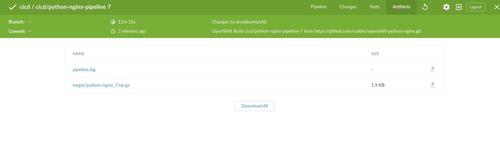
Python+NGINX running in DEV and STAGE project
You should see your server is up and running in DEV and STAGE Project.
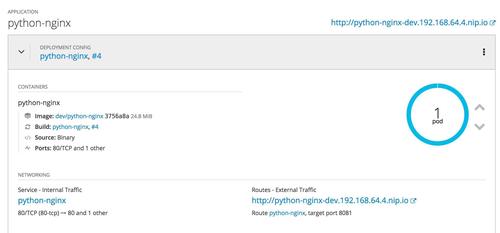
Automated deployment
Last part of our implementation is automated deployment. For that we are going to use Github Webhook. It will allow us to start a build based on an event in git repository. For starting a build, we need to define webhook triggers in Pipeline Build Config. We have defined triggers in our build config. Now we need to copy that trigger link from here:
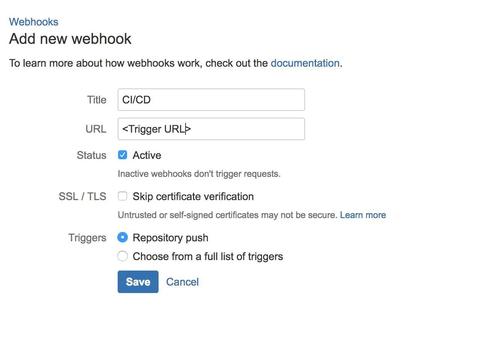
You can paste this webhook in your repository’s webhook settings, for example like this:
BitBucket
Github
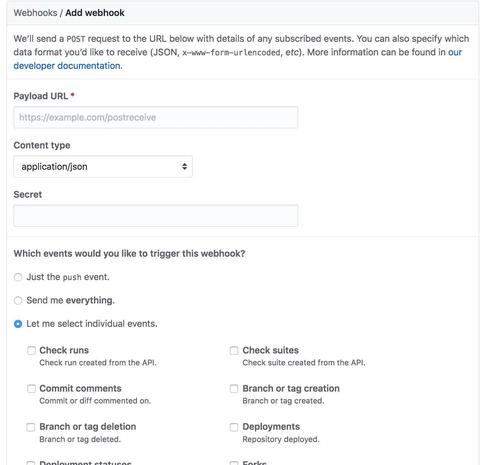
Then for any event(as per your configuration, like push, pull request merge etc) it will trigger a new build. FYI: this functionality will not work for minishift.
Working example
You will find a working example in my github repository.
Useful resources
- If you want to implement Django Using Pipeline, checkout my
openshift-djangorepo. - Read details about Jenkins Python Slave in in idealo’s repository.
- Read about running NGINX on OpenShift from torstenwalter.de.
- Read about CI/CD demo by RedHat in redhat’s github repository.
- For Python2.7 based deployment use this Jenkins Slave from dockerhub(developed by me).
Thank you for reading. Please let me know your feedback by commenting below.
Cheers!!
Last updated: May 04, 2025



Hi Rudra, I went through your blog on automated deployment from jenkins to openshift.I have followed the same steps and tried to import the yaml file in Openshift and started the pipeline.But not sure why I could not see any stages there. Kindly help me.
Hi @RekhaSabbineni22, its hard to say what it might be wrong without any codes. But maybe you can look into my repository: https://github.com/ruddra/openshift-python-nginx-pipeline and use it as boilerplate to implement your pipeline. Hope it helps
Hi Ruddra,
Great. Thanks for the information. This will help.
I need few clarification on below.
If you run using gunicorn or flask run with port. How we can expose route. Route is not working in OpenShift. Can you help me on this. If we go with node port. How we can do it.?
Well, you need to elaborate bit more on why route is not working.
Anyway, one possible reason why Routes not exposing is that, you are not exposing the port from docker. Please make sure you have
EXPOSE <PORT NUMBER>in your docker file.Finally, if you are using NodeJs, then you can write your own
Dockerfile. Here is an example from official documentation: https://nodejs.org/de/docs/guides/nodejs-docker-webapp/Well done!! Thank you so much for the tutorial. Helped me put everything in perspective!